Key Takeaways
- Data scientists gather information from a variety of sources, like spreadsheets, company databases, public websites, third-party tools, or sensors and devices.
- Data science combines programming, statistics, domain expertise, and problem-solving across many fields.
- Job growth for data scientists is strong, with a projected 36% increase this decade.
- Becoming a data scientist requires formal education, project work, and continuous skill-building.
We notice patterns all the time. Maybe a store seems to have sales at the same time each month, or certain posts show up more often after we search for something. These patterns become easy to spot once we know what to look for—and they can be really useful.
In data science, patterns go much deeper. They show up in huge datasets that track behavior, monitor systems, or record how things change over time. Finding those patterns and figuring out how to use them is a big part of what data scientists do.
What Is a Data Scientist?
A data scientist is an analytical expert who uses statistics, programming, and domain knowledge to extract insights from data. They explore information, look for patterns, test ideas, and use tools like statistics and programming to turn raw data into something useful.
Their work brings together skills from areas like mathematics, computing, research, and communication. Depending on the project, they might be analyzing customer behavior, building a forecasting model, or helping teams interpret the implications hidden in their data.
Although data science overlaps with several other roles in the field, the work of a data scientist is distinct. One area of confusion is the difference between data science and machine learning. While data scientists often use machine learning as part of their work, data science itself covers the entire process—from collecting and cleaning data to analyzing, modeling, and communicating results. Machine learning, by contrast, focuses specifically on the algorithms that learn patterns from data and make predictions. A data scientist might develop and test a model, while a machine learning engineer takes that model and makes sure it runs efficiently in real-world systems.
Another common question is about the difference between a data analyst and a data scientist. Data analysts typically examine past trends and produce reports that support business decisions. Data scientists go further by building predictive models, asking deeper questions, and working with larger, more complex datasets using advanced techniques.
What Does a Data Scientist Do?
Data scientists follow a workflow or process to solve data-related problems. While the specifics of the job vary by project, their work generally involves several key steps that build on one another.
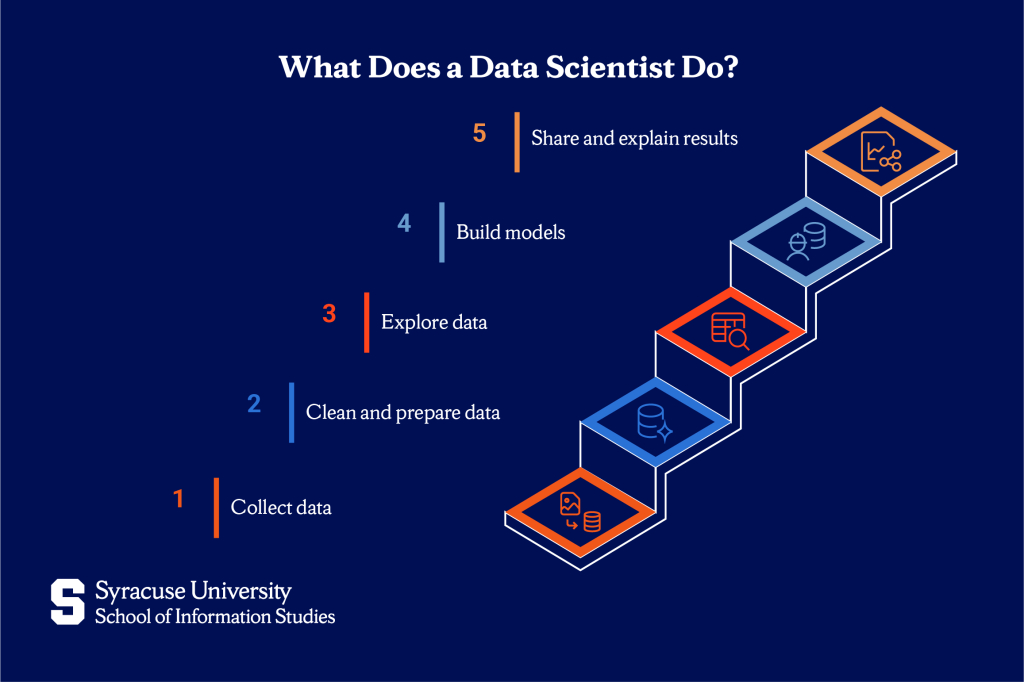
Collecting data
Data scientists gather information from a variety of sources, like spreadsheets, company databases, public websites, third-party tools, or sensors and devices. Some of the data might be collected automatically, while other parts require more manual effort. At this stage, the focus is on pulling together the right data for the task at hand.
Cleaning and preparing data
Real-world data can be incomplete, messy, or inconsistent. Therefore, data scientists spend a lot of time fixing errors, filling in missing details, and making sure everything is organized in a way that makes analysis possible. This step is important because clear, usable data leads to more trustworthy results.
Exploring the data
Exploring the data might include creating charts, running simple summaries, or comparing different trends across groups or time periods. The goal is to understand the basic shape of the data, identify any outliers or surprises, and figure out what questions are worth digging into further.
Building models
If the project involves prediction, grouping, or testing ideas, the data scientist will build a model. This means using statistics or machine learning tools to find patterns or estimate future outcomes. Depending on the goal, they might try different methods and compare how well each one performs. For example, they might build a model to estimate sales, recommend products, or predict equipment failures.
Sharing and explaining results
Once the analysis is complete, data scientists share what they’ve learned in ways that others can use. They might build dashboards, write reports, or present findings in meetings. A big part of this step is explaining the results clearly, especially to people who don’t work with data every day. Good communication helps make sure the insights lead to real improvements or decisions.
How to Become a Data Scientist
There’s more than one way to begin a career in data science. However, earning a degree often provides the strongest foundation, especially when paired with hands-on practice that reinforces key skills. Whether you’re starting from scratch or transitioning from another field, combining structured learning with real experience is one of the most effective ways to prepare for the responsibilities that await you.
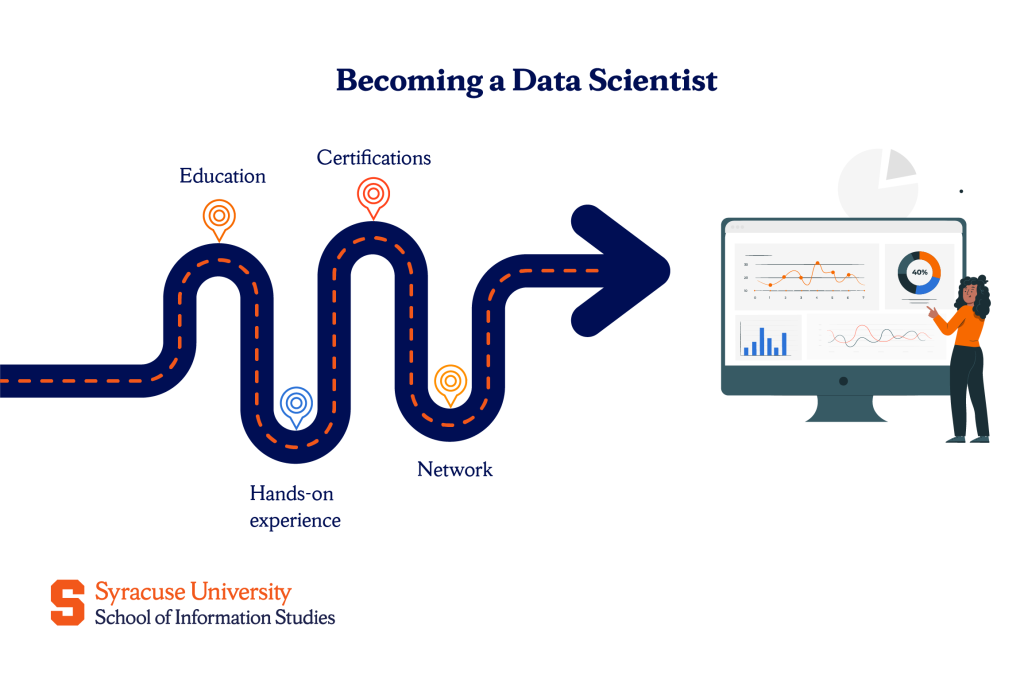
Start with the right education
Many data scientists begin with degrees in fields like computer science, statistics, or mathematics. These programs help build skills in logic, math, programming, and thinking critically about data.
For those looking for a more direct route into the field, a structured program like the Master of Applied Data Science at Syracuse University can help. It combines technical training with real-world problem-solving, preparing students to step into data science roles in as little as one year.
Get hands-on experience
One of the best ways to grow is by applying what you learn. This could include class projects that mimic real challenges, internships that expose you to business problems, group learning environments where you build solutions together, or capstone work that ties everything into a final deliverable.
Online platforms like Kaggle also let you experiment with public datasets, take part in competitions, and learn from other participants’ approaches. You can even explore your own ideas, contribute to open-source projects on GitHub, or take on freelance work that adds to your experience. The goal is to build confidence, expand your skill set, and understand how data is used in practical, varied contexts.
Explore certifications
Certifications can be a helpful way to structure your learning and show what you’ve accomplished. Platforms like Coursera, edX, and DataCamp offer a wide range of courses in data science, analytics, and machine learning.
If you’re looking for a more focused academic program, Syracuse University’s Certificate of Advanced Study in Data Science offers a shorter, graduate-level option that’s designed to help professionals strengthen their data skillset without committing to a full degree.
Build your portfolio and network
As you grow, keep track of your projects and put them somewhere others can see—like a personal website or GitHub. A simple portfolio with a few well-documented projects can help show employers what you’re capable of.
Networking also makes a difference. Join LinkedIn groups, attend meetups (virtual or local), and connect with others in the field. Many opportunities come through conversations, not just job boards.
Key Skills of a Data Scientist
The role of a data scientist blends analysis, creativity, and teamwork, so success often requires combining strong technical abilities with communication and problem-solving.
Technical skills
Data scientists rely on a wide range of tools and methods to work efficiently and solve different types of problems. Therefore, their technical skills are centered on knowledge and experience using:
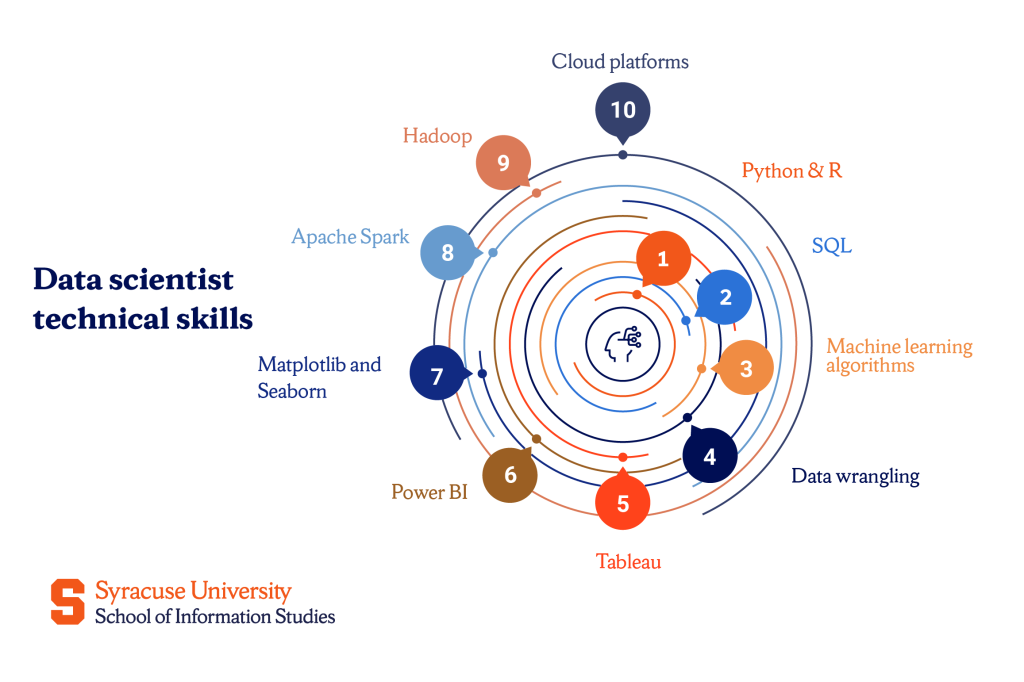
- Python & R
- SQL
- Machine learning algorithms
- Data wrangling
- Tableau
- Power BI
- Matplotlib and Seaborn
- Apache Spark
- Hadoop
- Cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure
Soft skills
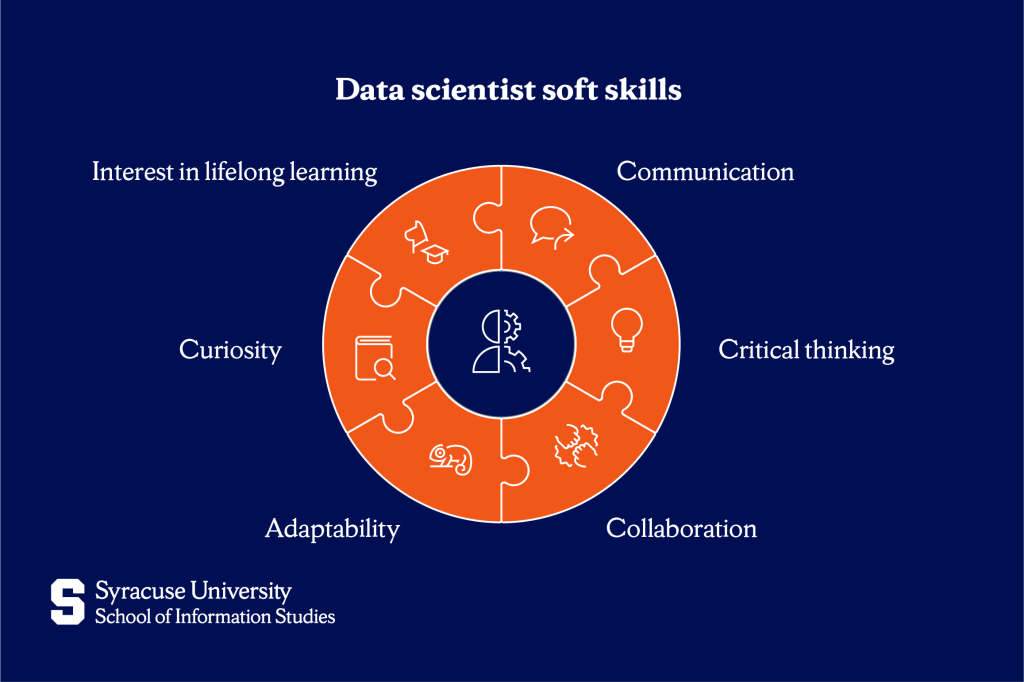
In addition to technical knowledge, data scientists benefit from soft skills that help them communicate effectively, think critically, and adapt to new challenges. These include:
- Communication
- Critical thinking
- Collaboration
- Adaptability
- Curiosity
- Interest in lifelong learning
Where Do Data Scientists Work?
Data scientists are in demand across many industries, and their roles span a wide range of sectors. In 2023, there were approximately 202,900 data science jobs, with the largest employers including:
- Computer systems design and related services
- Insurance carriers and related activities
- Management of companies and enterprises
- Management, scientific, and technical consulting services
- Scientific research and development services
What makes this role so adaptable is that data is everywhere. No matter the industry, organizations need people who can make sense of their information and help guide decisions. The specific questions being asked might vary, and the nature of the work may differ depending on the setting. In tech or finance, projects often move fast and involve real-time data. In healthcare or research, data scientists may spend more time analyzing long-term trends or working with sensitive information.
Still, the core of the work stays the same across all industries; the value they bring lies in helping teams move more strategically and base their decisions on evidence instead of guesswork.
Data Scientist Salary & Career Outlook
Data science offers strong career prospects in terms of job growth and salary. In fact, this role has often been cited as one of the top jobs of the 21st century for its combination of high demand, high pay, and job satisfaction.
The median annual salary for data scientists is estimated to be $112,590. Generally, six-figure salaries are common in this field, especially after gaining a few years of experience in the field.
In terms of career outlook, the employment of data scientists is expected to grow 36% from 2023 to 2033—much faster than the average for most occupations. This high demand is driven by the fact that organizations across all sectors are collecting more data than ever and are keen to derive insights from it.
Your Path Forward in Data Science
Anyone can spot a few patterns, but it takes a skilled data scientist to find the right ones and turn them into insight, action, impact, and long-term value.
What sets the most successful data scientists apart isn’t just what they know—it’s how they think. They question assumptions, explore unfamiliar problems, stay open to new tools, and continue learning long after they’ve mastered the basics. That kind of mindset takes time, structure, and support to develop.
A strong academic foundation can offer all of that. At the iSchool at Syracuse University, our programs are designed to help you build skills, sharpen your thinking, and grow into a role that evolves as fast as the field itself. So, if you’re ready to work with data in ways that matter, this is the place to start.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is it hard to become a data scientist?
Becoming a data scientist can be challenging for some, but with steady learning and hands-on practice, many people from different backgrounds successfully make the switch. The key is consistency and using the right resources to build your skills over time.
Can I transition from another career into data science?
Certainly! Many data scientists come from other fields like business, engineering, or research. Your existing experience can be an asset once you learn the core data skills.
What industries pay the most for data scientists?
Tech and finance typically offer the highest salaries. Roles in software, consulting, and enterprise management also tend to pay well.
