Key Takeaways
- AI improves efficiency, productivity, decision-making, innovation, and customer experience across various sectors.
- AI is applied in fields like healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, and cybersecurity.
- Ethical concerns, bias, and transparency must be considered when developing and implementing AI.
In 2025, the market for AI (artificial intelligence) technologies reached an estimated value of 244 billion U.S. dollars. But what’s even more impressive is that it’s projected to go over 800 billion U.S. dollars by 2030.
It’s no surprise, then, that a staggering 90% of companies worldwide are either already utilizing AI or looking into how they can incorporate it.
So, why are so many organizations eager to embrace AI? The answer is clear: it’s all about the remarkable benefits of AI.
Major Benefits of AI
The advantages of artificial intelligence are key to helping companies stay ahead of the curve. Some of the most transformative benefits include:
Increased efficiency & productivity
AI enhances business operations by automating repetitive tasks, allowing human workers to focus on other work that may be more complex and require human involvement. Tasks like scheduling meetings or generating reports, which are often time-consuming, can be automated by AI systems.
This automation, in addition to saving time, increases productivity across teams. For example, AI-powered tools that assist with scheduling or automating routine reporting tasks are improving office productivity, enabling workers to allocate their time toward more high-value activities.
A study showed that AI-powered customer support agents could handle 13.8% more inquiries per hour compared to traditional methods while also improving work quality by 1.3%.
Additionally, implementing generative AI tools leads to an average performance improvement of 66%, with even greater gains for complex tasks.
This surge in efficiency and productivity reflects AI’s transformative potential in empowering employees and making businesses more responsive in today’s competitive environment.
Enhanced decision-making & data analysis
AI’s ability to analyze large amounts of data in a short amount of time allows businesses to make well-informed decisions without the need for extensive human resources.
In industries such as finance, AI is already being used to analyze trends and help businesses understand markets in ways that would be far more time-consuming and complex for humans to analyze manually.
AI-driven systems excel at detecting patterns in data, making them valuable for fraud detection and risk assessment while also minimizing the risk of human error.
This level of analysis helps prevent financial crimes as well as empowers businesses to make more accurate decisions regarding investments, customer engagement, and overall strategies.
Improved customer experience
From personalized recommendations on platforms like Netflix and Amazon to virtual assistants handling customer queries, AI has transformed how businesses interact with their customers.
AI-powered personalization enhances customer satisfaction by anticipating needs based on behavioral data and preferences.
For example, businesses that use AI-powered chatbots can now offer 24/7 customer support so that their customers can receive instant responses to inquiries at any time of day. A survey by Salesforce found that an impressive 84% of salespeople who are already using AI report that it has helped increase sales by enhancing and accelerating customer interactions. Similarly, 90% of service professionals using it confirm it helps them serve customers faster.
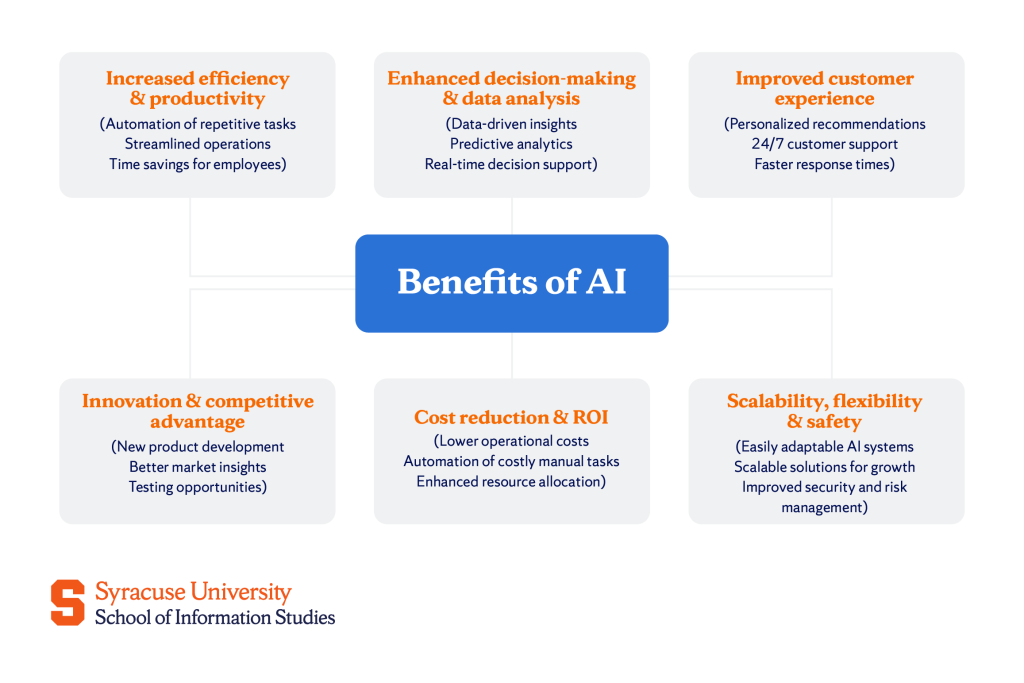
Innovation & competitive advantage
Through its ability to quickly process large volumes of data, AI can fast-track the pace of discovery and invention.
An example of this capability is AlphaFold, an AI model developed by Google DeepMind, which accurately predicts the structures of thousands of proteins. This breakthrough is opening up new avenues for understanding diseases and creating targeted treatments for conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Businesses are also using AI to gain a competitive edge by innovating more efficiently than their competitors. For example, Danone, a multinational food products company, incorporated AI to revitalize its yogurt business.
Faced with increasing competition and market stagnation, Danone turned to AI to analyze large datasets, identify emerging consumer preferences, and predict new product trends. By using AI to test product formulations and predict customer demand, the company was able to gain a competitive advantage.
Cost reduction & return on investment (ROI)
AI presents significant opportunities for businesses to reduce operational costs while maximizing efficiency. By streamlining workflows, accelerating decision-making, and processing large datasets far faster than humans, AI contributes to substantial cost savings.
A study conducted by McKinsey highlighted that AI-driven automation can lead to significant cost reductions for businesses, particularly in human resources. Additionally, the study found that supply chain and inventory management see the highest revenue increases, with more than 5% growth reported by the majority of respondents.
When it comes to analytical AI, the greatest cost benefits are observed in service operations, while marketing and sales report the most substantial revenue growth from AI adoption.
Scalability, flexibility & safety
AI helps businesses scale efficiently and maintain safety in high-risk environments. For instance, cloud-based AI solutions allow companies to expand their capabilities without requiring significant infrastructure investments.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has been using AI tools to improve its ability to detect anomalies in network data and protect critical infrastructure.
AI’s ability to continuously monitor network traffic and then quickly adapt to new security challenges is essential for organizations operating in high-risk environments. CISA has been using AI for tasks such as malware reverse engineering, anomaly detection, and automated detection of personally identifiable information (PII)—all of which help prevent and mitigate cyberattacks.
Industry-Specific Applications
AI is highly adaptable and can be customized to address unique challenges across various industries. Key applications include:
Healthcare
AI in healthcare is primarily applied to improving diagnostics and patient outcomes by:
- Analyzing X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans for abnormalities.
- Predicting patient risks and suggesting personalized treatments.
- Automating scheduling, billing, and other administrative tasks.
- Assisting in robotic surgery by automating tasks like suturing and tissue dissection.
Finance & economic growth
In the finance sector, AI is used to enhance economic growth by:
- Improving market forecasts and risk assessments through advanced predictive analytics.
- Detecting fraud by analyzing transaction patterns for suspicious activity in real-time.
- Supporting customer service with chatbots and improving credit scoring models.
- Helping clients make informed investment decisions with AI-powered robo-advisors.
Retail & ecommerce
In retail and e-commerce, AI improves customer experience and operational efficiency by:
- Providing personalized product recommendations.
- Managing inventory by predicting demand.
- Optimizing prices by analyzing market trends and competitor pricing.
- Offering real-time customer support through AI-powered chatbots.
Manufacturing & engineering
In the manufacturing and engineering sectors, AI is driving transformative changes by:
- Utilizing predictive maintenance systems to detect potential machinery failures.
- Simulating complex systems to improve product designs.
- Optimizing supply chains by predicting demand and streamlining inventory management.
Transportation & smart cities
AI is transforming the transportation sector and smart cities by:
- Enabling autonomous vehicles such as self-driving cars, trucks, and drones to navigate without human intervention.
- Optimizing traffic management systems to reduce congestion and improve route planning.
- Managing resources efficiently in smart cities, including monitoring energy consumption, improving waste management, and ensuring public safety through real-time surveillance.
- Predicting delays and providing optimal routes for commuters.
Agriculture & sustainability
AI is revolutionizing agriculture and sustainability by:
- Implementing precision agriculture through weather pattern analysis, soil condition monitoring, and crop health assessments..
- Using AI-powered drones and robots for crop monitoring and harvesting.
- Tracking water usage and carbon emissions to support environmental sustainability efforts.
Cybersecurity & surveillance
AI enhances security and surveillance by:
- Detecting anomalies and identifying potential threats in real-time.
- Improving threat detection accuracy through pattern recognition in large datasets.
- Monitoring public and private spaces for suspicious activities.
- Recognizing faces, detecting unusual behavior, and alerting authorities instantly.
Challenges and Considerations
With the immense potential of AI, there are certain factors that must be addressed. It is important for developers and organizations alike to guarantee that AI is used responsibly.
Ethical considerations
Ethical considerations in AI, especially regarding AI bias, privacy, and fairness, are essential.
Bias in AI can arise from the data used to train models or from the algorithms themselves, leading to unfair decision-making—particularly in critical areas like hiring, lending, and law enforcement.
Privacy risks emerge when AI systems handle personal or sensitive data, requiring strict safeguards to prevent misuse.
Transparency and interpretability are essential so that AI-driven decisions remain understandable, explainable, and aligned with ethical standards.
Implementation barriers
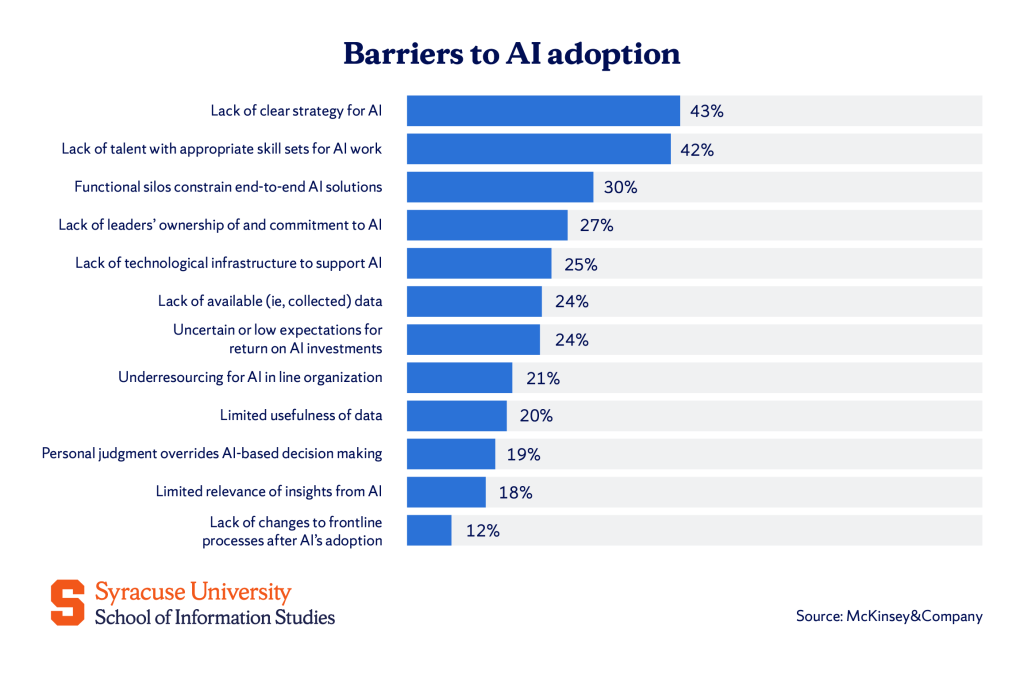
Results from a survey conducted by McKinsey & Company showed that the most common challenge in implementing AI solutions within their organizations is the lack of a clear AI strategy (43%). Many struggle to define a cohesive and well-structured strategy for implementing AI.
This is closely followed by the shortage of appropriate talent (42%), as there is a gap in skilled professionals with the expertise needed to drive AI initiatives.
To address the challenges in implementing AI, organizations should start by developing a clear AI strategy that aligns with business goals. They should invest in training their workforce to bridge the talent gap, while also collaborating across departments to break down silos.
Leadership must always actively support AI initiatives and demonstrate commitment to providing the needed resources for successful adoption and integration.
Job displacement
Job displacement due to AI technologies is a legitimate concern for many, and it’s certainly something that needs careful consideration. While it’s true that up to 300 million jobs could be impacted by AI, the rise of these technologies will also create hundreds of new job categories.
The overall global productivity is projected to increase by around 7% annually over the next 10 years. This shift presents an opportunity for innovation rather than a threat.
Final Reflections on AI
At Syracuse University’s iSchool, our faculty are conducting cutting-edge research on AI and data science, exploring the far-reaching impact of these technologies on industries and societies. A prime example is our Critical AI Research and Education (CAIRE) Lab, an interdisciplinary space that investigates the historical, geopolitical, material, spatial, and social dimensions of data, information, and technology. This work positions us at the forefront of AI research and provides valuable insights into its future.
For those eager to learn about AI and actively contribute to its advancement, we invite you to explore our Master’s degree program in Artificial Intelligence. Beyond a strong theoretical foundation, students have access to student-led consulting projects, research endeavors, internships, and networking events with AI industry leaders.
These experiences equip students with the tools to take the next step in their careers and become leaders in AI innovation.
As businesses explore and benefit from the vast potential of AI, it’s students and researchers in this field who will drive innovation and ensure AI’s responsible and ethical development for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the pros and cons of AI?
AI offers numerous benefits, such as enhancing efficiency and productivity and improving decision-making across industries. However, challenges remain, including job displacement, the potential for algorithmic bias, and ethical concerns that require careful oversight.
What are some AI applications in everyday life?
You’ll probably come across AI in various ways daily—whether it’s through virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, getting personalized recommendations from Netflix or Amazon, or even in the growing presence of self-driving cars and targeted ads you see online.
What are the benefits of using generative AI (GenAI) in cybersecurity?
GenAI enhances cybersecurity by improving threat detection, accelerating incident response, and increasing prediction accuracy, which can make systems more resilient against cyber threats.
Will AI make most HR functions irrelevant in the near future?
AI can automate routine HR tasks like resume screening, but it cannot replace human judgment in hiring, employee development, or workplace culture management. Instead, AI serves as a tool to enhance efficiency, allowing HR professionals to focus on strategic, people-centric responsibilities.
